Notes for Mesa
Overview
Mesa 包含了各种 GPU/CPU 的 OpenGL, OpenCL, Vulkan 实现(Usermode Driver), 也包括 GLX, EGL, GBM 等协议的实现。
- Vulkan 驱动
| codename | directories | platforms |
|---|---|---|
| anv | src/intel/vulkan, src/intel/vulkan_hasvk | Alder Lake-P |
| asahi | src/asahi/vulkan | Apple M1, M2 |
| lpv | src/gallium/drivers/llvmpipe | CPU |
| panvk | src/panfrost/vulkan | RK3399 |
| v3dv | src/broadcom/vulkan | Raspberry Pi |
Build
Build Dependencies (since mesa-25.0.0)
| dep | apt-get | version required | yet another install | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /usr/bin/glslangValidator | glslang-tools | https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glslang | ||
| /usr/bin/rustc | rustc | 1.78.0 or newer | `curl --proto ‘=https’ --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | |
| bindgen (rust package) | cargo | 0.65 or newer | cargo install bindgen-cli |
|
| libclc-dev | libclc-17-dev | not required if -Dmesa-clc=auto | ||
| + | libdrm | libdrm-dev | 2.4.121(120 ok2.0) | https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/mesa/drm |
| llvm | llvm-17-dev | (17.0.6 ok2.0) | https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project | |
| libLLVMSPIRVLib.so.17 | llvm-spirv-17 | (17.0.0 ok2.0) | https://github.com/KhronosGroup/SPIRV-LLVM-Translator | |
| + | LLVMSPIRVLib.h | llvmspirvlib-17-dev | (absent ok2.0) | https://github.com/KhronosGroup/SPIRV-LLVM-Translator |
| clang-cpp | libclang-cpp17-dev | (17.0.6 ok2.0) | not required if -Dmesa-clc=auto | |
| * | clang-dev | libclang-17-dev | Debian package issue | |
| xshmfence | libxshmfence-dev | (1.3 ok2.0) | required if -Dplatforms=x11 | |
| xxf86vm | libxxf86vm-dev | (1.1.4 ok2.0) | required since -Dglx-direct=true by default | |
| xrandr | libxrandr-dev | (1.5.2 ok2.0) | required since -Dxlib-lease=true | |
| cbindgen (rust package) | cargo | 0.28.0 | cargo install cbindgen; required if -Dgallium-drivers=nouveau |
NOTE:
-
(*) 表示本来不需要的依赖
-
(+) 在 OpenKylin 2.0 的源里没有,需要源码构建
-
Ubuntu 22.04
书到用时方恨少,包要装时不好找
1 | sudo apt install -y cmake ninja-build bison flex g++ git pkg-config python3-setuptools python3-lz4 \ |
1 | meson build -Dprefix=/usr/local -Dlibdir=lib/x86_64-linux-gnu -Dplatforms=x11 -Dgallium-drivers=nouveau |
-Dprefix=/usr/local避免覆盖系统原来的libGL*-Dlibdir=lib/x86_64-linux-gnu设置库的安装路径为/etc/ld.so.conf.d/x86_64-linux-gnu.conf中搜索第一顺位的路径- 其他默认就好, 出现的依赖在 OpenKylin 2.0 上 apt-get 基本都能解决
1 | Build targets in project: 437 |
After compilation and installed as follow:
1 | ls -l /usr/local/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu |
NOTE:
- Mesa is installed in
/usr/local/lib/$(uname -p)-linux-gnuby default. So you have toldconfigso that your linker can find them. - libsoftpipe.a will be built but not installed.
- meson build system will enable compiler’s
-gflag by default unless you are building on the release branch. - if you have remodified the meson_options.txt and built once and now are about to reconfigure and rebuild, you need to run:
1 | meson setup --wipe build |
与 mesa 相关的一些常用软件包
mesa-utils
包含以下 glx demo 或 test program
- glxdemo
- glxgears
- glxheads
- glxinfo
mesa-utils-extra
包含以下 egl demo 或 test program
- eglinfo
- es2_info
- es2gears_wayland
- es2gears_x11
- es2tri
Off-screen Demos
Now that mesa have been built and installed we can give a try to run an OGL application. Similarly without window system supportd on the WSL, off-screen rendering is my choice. We can clone the mesa demos which includes a lot of demos besides off-screen demos.
Requisite
We need some more libraries besides libOSMesa and libGL before you can get these off-screen demos worked. They are:
- GLU
- libm
To build these demos:
1 | gcc osdemo.c -o osdemo -g -I/home/luc/github/demos/src/util -lGL -lGLU -lOSMesa -lm |
The executable osdemo saves the rendered pixels as the portable pixmap format. You need to covert it to image format e.g. jpg. You may do this with pnmtojpeg output.ppm > output.jpg.

OSMesa Call Graphs
Mesa supports many features from software pipelines to hardware drivers. For example Gallium, it features with several software or hardware implementations which include the two software pipelines, softpipe and llvmpipe. With the different pipes enabled will the calls walk in the different paths.
Three Different Build Configuration (reference to meson_options.txt)
| Option | platform | glx | dri-drivers | gallium-drivers | llvm | osmesa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| llvmpipe | x11 | gallium-xlib | swrast | true | gallium | |
| softpipe | x11 | gallium-xlib | swrast | false | gallium | |
| tnl | x11 | gallium-xlib | swrast | true | classic |
Three Different Call Paths
Context

NOTE: As for softpipe and llvmpipe gl_api and gl_context are created respectively while both of them are created in one path for the classic osmesa.
Draw
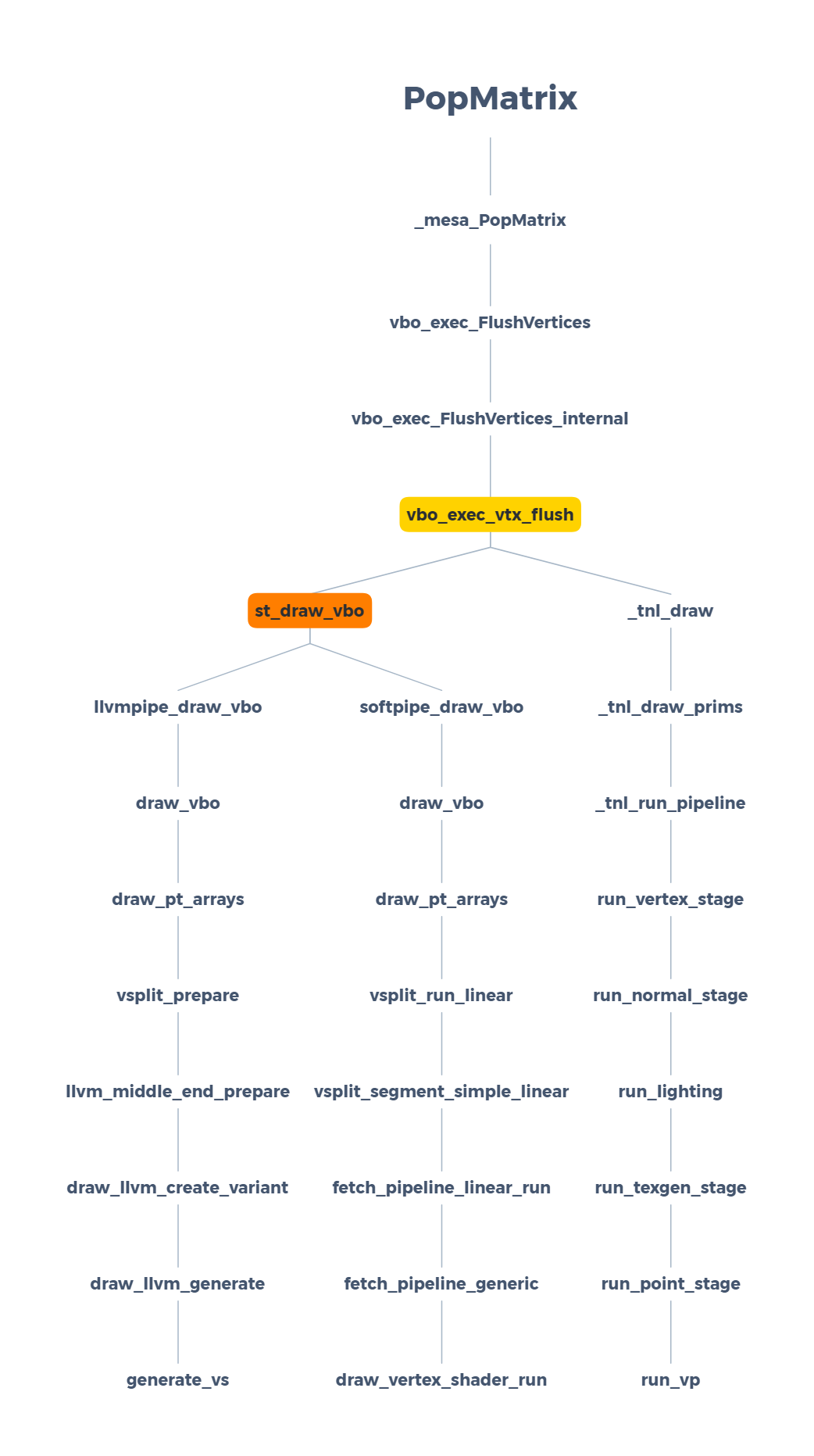
Gallium-Based GLX Demos
If you want to know the full graphic stack of an OpenGL demo, you can not get rid of the window system. That is why I will try some GLX demos. Evidently GLX demos must depend on X11. You can cope with this problem by installing vcXsrv on the Windows 10 which hosts your WSL.

This time I still choose the gallium-xlib with softpipe. The following call graph shows the path that GLX context is created.
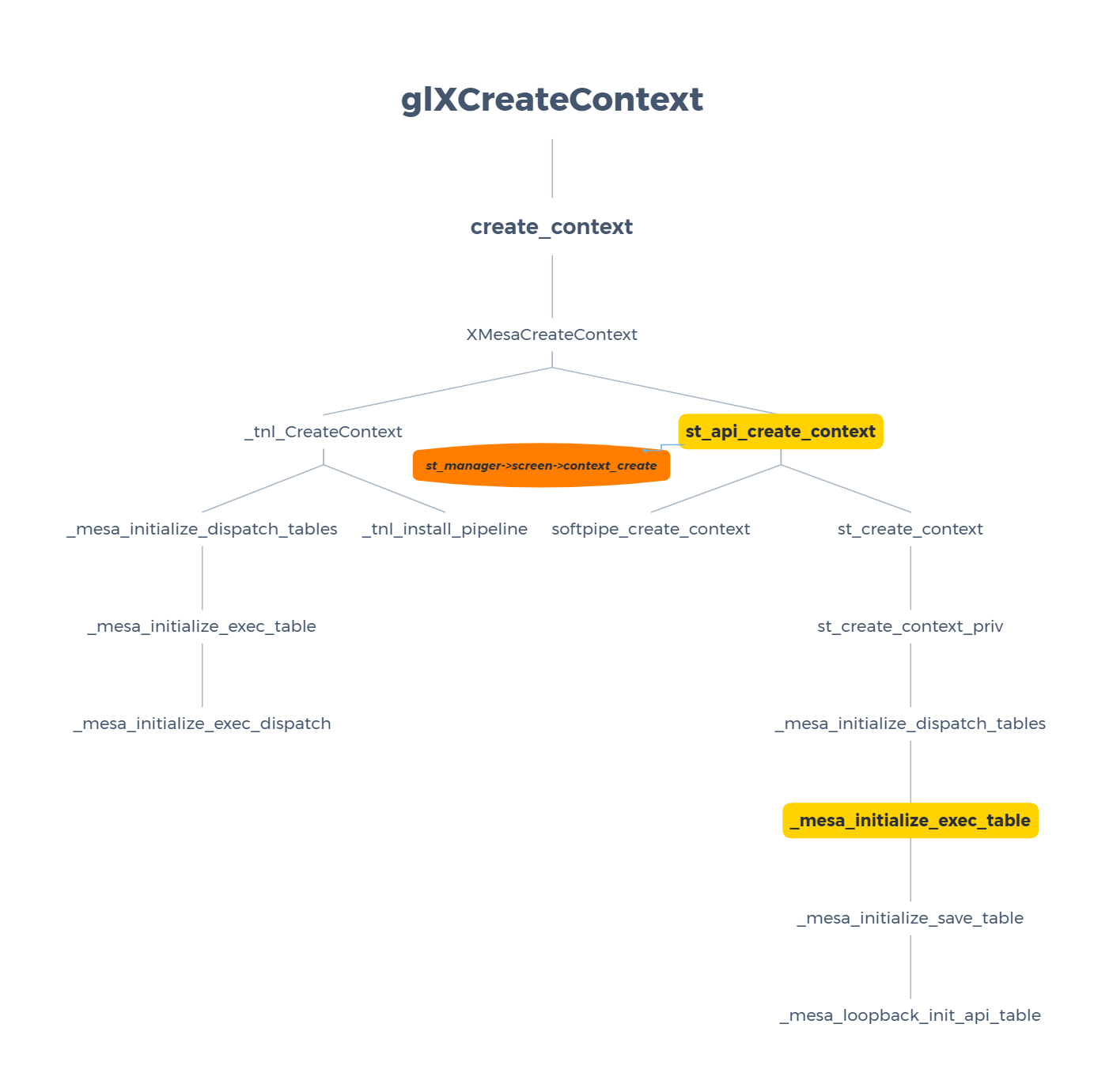
As we know, Mesa is quite modularized and flexible. How does it take the path that softpipe_create_context rather than other pipe contexts? The st_manager is a key structure.
struct pipe_screen has a callback function that will be set to softpipe_create_context. The following calls will create struct pipe_screen that will be set to the st_manager.
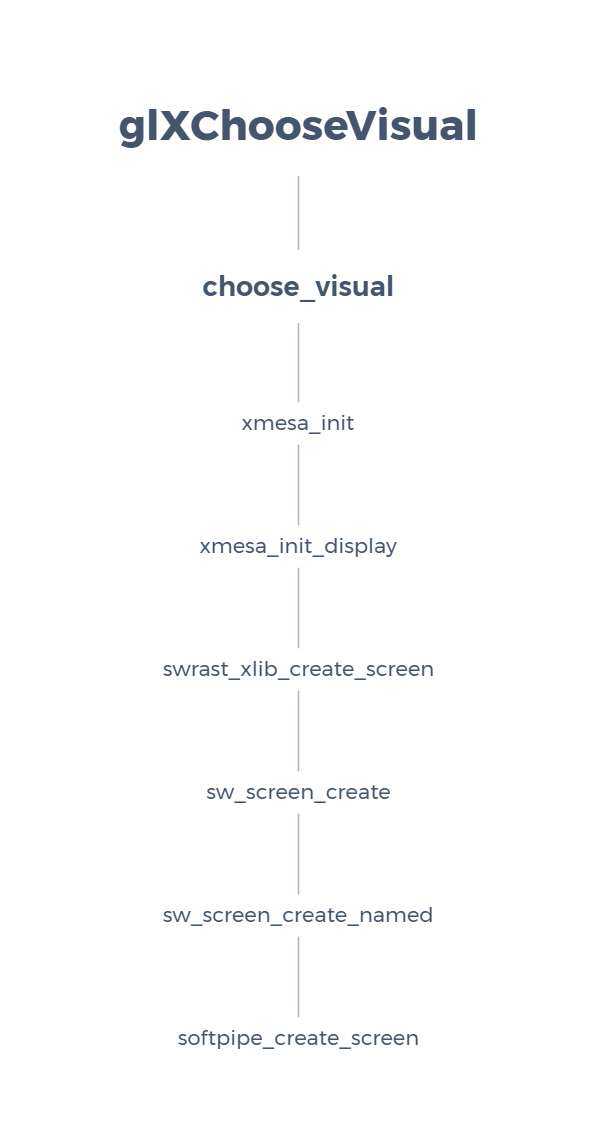
To bind the intended gallium driver backend to Mesa there must be something done before glXChooseVisual is called. It’s started by the library init() and prepare the global variables.
1 | /* This is the driver interface required by the glx/xlib state tracker. |
DRI-Based GLX Demos
Loading
__glXInitializedriOpenDriver
This process of loading drivers works similarly with that of gallium-based glx. Compilation macros and environment variables make a difference. There are several approaches to load the specific drivers:
dri3_create_displaydri2CreateDisplaydriCreateDisplaydriswCreateDisplayapplegl_create_displaydriwindowsCreateDisplay
Let’s look into driCreateDisplay. Once it manages to attach to driCreateScreen which searches and matches the appropriate gallium driver the function driOpenDriver will open the found driver by its name like “i965”, “radeon”, “nouveau”, etc. These drivers are supposed to be installed at LIBGL_DRIVERS_PATH or LIBGL_DRIVERS_DIR(deprecated) and named as *_dri.so by default.
Like Gallium-based GLX’s _init routine with GCC constructor attribute, DRI-based GLX also defines a routine megadriver_stub_init with constructor attribute which allows to load the specific driver in a way of __DRIextension.
Contexts
There are a variety of contexts in Mesa. They are designed as a framework of layers.
1 | __________________ |
gl_context
This is the central context data structure for Mesa. Almost all OpenGL state is contained in this structure. Think of this as a base class from which device drivers will derive sub classes.
Apart from OpenGL state it contains several other contexts
swrast_contextswsetup_contextswtnl_contextvbo_contextst_context
st_context
draw_context
vbo_context
VBO is short for vertex buffer object. This context derives two kinds of vbo contexts, vbo_exec_context and vbo_save_context which vbo_exec_context is generic for core and compatible ogl and the other is specific for compatible ogl.
vbo_exec_vtx_init
- Allocate a
gl_buffer_objectwhich just is referenced. - Initialize vbo attributes including size, type and active size.
vbo vs. vao
1 | struct gl_buffer_object |
Dispatchers
Exec: The current dispatch table for non-displaylist-saving execution, either BeginEnd or OutsideBeginEndOutsideBeginEnd: The normal dispatch table for non-displaylist-saving, non-begin/endSave: The dispatch table used between glNewList() and glEndList()BeginEnd: The dispatch table used between glBegin() and glEnd() (outside of a display list). Only valid functions between those two are set, which is mostly just the set in a GLvertexformat struct.ContextLost: Dispatch table for when a graphics reset has happened.MarshalExec: Dispatch table used to marshal API calls from the client program to a separate server thread. NULL if API calls are not being marshalled to another thread.CurrentClientDispatch: Dispatch table currently in use for fielding API calls from the client program. If API calls are being marshalled to another thread, this refers toMarshalExec. Otherwise it refers toCurrentServerDispatch.CurrentServerDispatch: Dispatch table currently in use for performing API calls. It refers toSaveorExec.
Modules
- draw module
- CSO module
- translate module
- VBO module
- TNL module(Transform & Light)
draw_xxx_stage
extern struct draw_stage *draw_unfilled_stage( struct draw_context *context );extern struct draw_stage *draw_twoside_stage( struct draw_context *context );extern struct draw_stage *draw_offset_stage( struct draw_context *context );extern struct draw_stage *draw_clip_stage( struct draw_context *context );extern struct draw_stage *draw_flatshade_stage( struct draw_context *context );extern struct draw_stage *draw_cull_stage( struct draw_context *context );extern struct draw_stage *draw_stipple_stage( struct draw_context *context );extern struct draw_stage *draw_wide_line_stage( struct draw_context *context );extern struct draw_stage *draw_wide_point_stage( struct draw_context *context );extern struct draw_stage *draw_validate_stage( struct draw_context *context );
Auxiliary
-
cso_cache
The CSO cache is used to accelerate preparation of state by saving driver-specific state structure for later use. -
draw
Draw is a software TCL pipeline for hardware that lacks vertex shaders or other essential parts of pre-rasterization vertex preparation. -
driver_ddebug
-
driver_noop
-
driver_rbug
-
driver_trace
-
gallivm
-
hud
-
indices
Indices provides tools for translating or generating element indices for use with element-based rendering. -
nir
-
os
- memory allocation
- simple message logging
- obtaining run-time configuration option
- threading primitives
The OS module contains the abstraction for basic operating system services above. This is the bare minimum required to port Gallium to a new platform. It already provides the implementations of these abstractions for the most common platforms. When targeting an embedded platform no implementation will be provided - these must be provided separately.
-
pipe-loader
-
pipebuffer
-
postprocess
-
rbug
-
renderonly
-
rtasm
-
target-helpers
-
tgsi
-
translate
-
util
-
vl
Q&A
- When xlib creates pipe screen, only software rasterizers or pipes’screen are created. And llvmpipe, softpipe, virgl, swr, unexceptionally, are software rasterizers or virtual GPU. Zink is, in brief, a translator from OpenGL to Vulkan and implemented as Gallium driver. So why only software pipes?
The answer is sw_winsys. All of target helpers’s parameter is a sw_winsys. Check mesa source directory: mesa/src/gallium/winsys
1 | amdgpu |
To put it simply, specific driver corresponds to specific winsys. The sw is for software rasterizers. If you expect to create pipe screen for some driver else, you need to add another target helper with its winsys as parameter like:
1 | static inline struct pipe_screen * |
That means you have to declare a bunch of new interfaces from the top. So you’d better wrap the function to create specific driver’s winsys so that it can take a sw_winsys as its parameter like:
1 | #if defined(GALLIUM_VIRGL) |
- libGL.so is not built until glx option is enabled in meson_options.txt.
Only with essential build-time dependencies for X11 installed and glx option configured is libGL.so built.
- What role do DRM, DRI and Gallium play in Mesa?
1 | _libdrm_checks = [ |
DRI and Gallium seem to be respectively different underlying implementation in Mesa. Moreover in term of swrast and i915, you have to choose either of both as you can read the following code snippet in meson.build. In fact DRI is more complicated and staler but Gallium is more smaller and simpler.
1 | if with_dri_swrast and (with_gallium_softpipe or with_gallium_swr) |
-
What problems are encountered when you build mesa on the WSL?
-
dri based GLX requires shared-glapi
-
Gallium-xlib based GLX requires softpipe or llvmpipe
- means that
gallium-xlibis supposed to only support software rasterizers(llvmpipe, softpipe) and virtual GPU(virgl, swr).
- means that
1 | option( |
In Mesa, glx is implemented in three ways:
| *-based | backend | window system |
|---|---|---|
| dri-based | non-sw-pipes | *_drm_winsys |
| xlib | tnl | sw_winsys |
| gallium-based | softpipe/llvmpipe | sw_winsys |
- OSMesa gallium requires gallium softpipe or llvmpipe
- means if
osmesais configured asgallium,gallium-driversmust includeswrastbut theclassicosmesa uses the fixed-functioned TNL by default.
- means if
1 | option( |
-
Cannot build GLX support without X11 platform support and at least one OpenGL API
- GLX, As the name suggests, is dedicated to X11 winsys.
-
When
__glXInitializecreates theDisplay, onlydriswCreateDisplayreturns successfully. Both ofdri2CreateDisplayanddriCreateDisplayfailed. -
env: WSL on Windows 10 and with vcXsrv installed on the host as X server
The cause of failure is that vcXsrv has no extensions with DRI or DRI2. This lack of X server extension fails DRI2QueryExtension and XF86DRIQueryExtension so that the loading of gallium driver is not invoked.
Debug
环境变量
- MESA_VERBOSE=comma-separated-list
- MESA_VERBOSE=api
- MESA_GLSL=comma-separated-list
MESA_GLSL=log把所有 GLSL shader 保存到文件里, shader_X.vert 或 shader_X.frag