Smart Pointer
smart pointer是C11引入的,被包含在C标准库中。smart pointer是为了管理对象的所属(object ownership)而设计的,smart pointer对象负责自动地销毁所关联对象。常见的smart pointer有:
std::shared_ptrstd::unique_ptrstd::weak_ptr
shared_ptr
shared_ptr主要用在多个对象共享同一个资源的场景(sharing ownership)。它允许当指针指向的对象在任何地方都不再被使用的时候自动销毁所指对象。C++引入它的目的是消除内存泄漏(memory leak)和野指针(dangling pointer). 从实现的角度看,shared_ptr是通过消耗更多的内存来换取程序的健壮性。每个shared_ptr对象的内部都指向两块内存区域:
- Pointer to object
- Pointer to control data that is used for reference counting
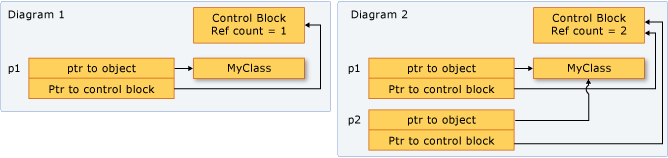
通常一个shared_ptr对象的内存大小不小于40字节,这是32位平台普通指针变量大小的10倍。shared_ptr的destructor和虚成员函数意味着这些成员函数的调用是动态解析的,这就增加了额外的运行时开销。
creation
-
binding a
shared_ptrobject with raw pointerstd::shared_ptr<int> p1(new int()); -
using
std::make_sharedstd::shared_ptr<int> p1 = std::make_shared<int>();
reference counting
p1.use_count();
detachment
-
calling
reset()with no parameterp1.reset();这个调用将
p1的reference count减1, 如果reference count变成0,则自动删除p1关联的raw pointer. -
calling
reset()with parameterp1.reset(new int(42));这个调用将
p1关联到一个新的raw pointer, 因此p1的reference count还是1. -
using
nullptrp1 = nullptr;
psuedo pointer
unique_ptr
unique_ptr同样是为了管理对象的所属(unique ownership),但与shared_ptr相反,unique_ptr允许在程序的生命周期的任何时候只有一个指针指向对象,所以unique_ptr是不可复制的。